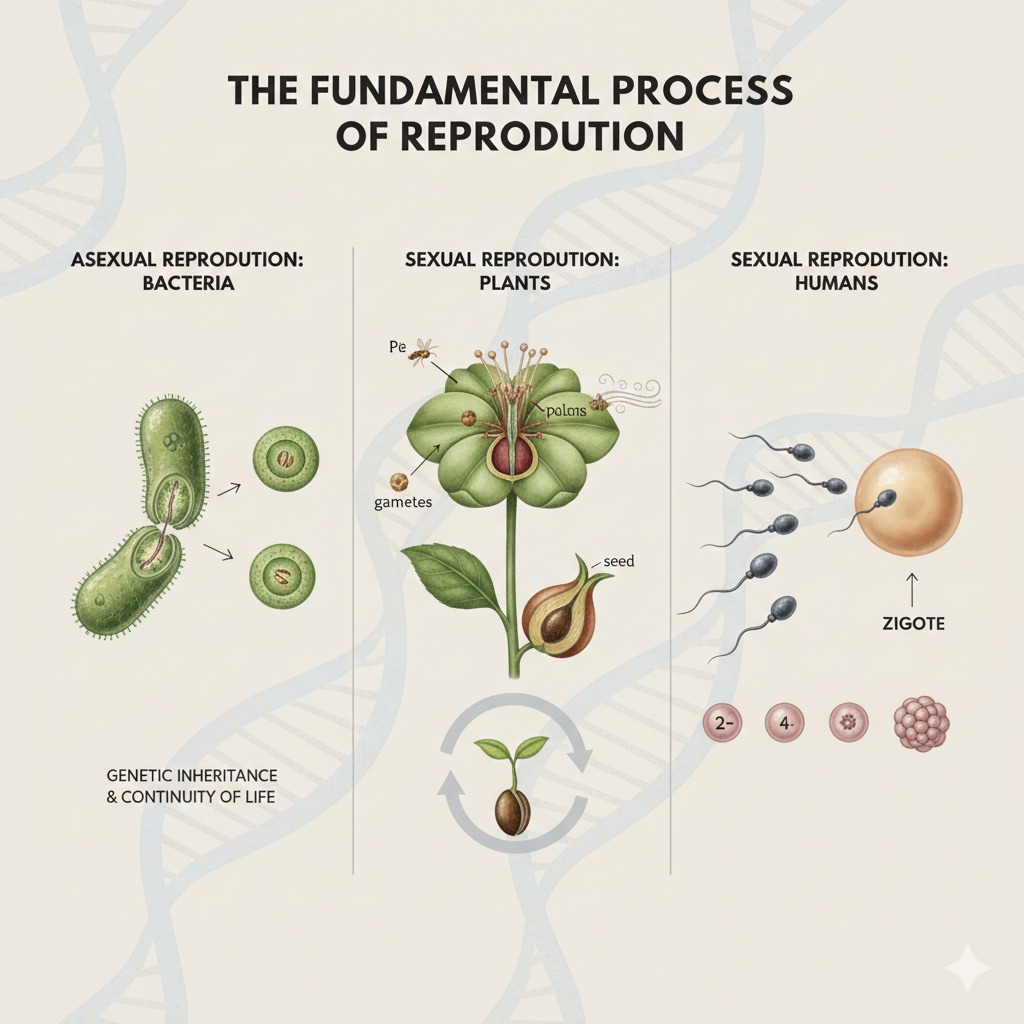
Reproduction is one of the most fundamental characteristics of all living organisms. Without reproduction, life on Earth would not continue beyond a single generation. In biology, reproduction refers to the process by which organisms produce new individuals of the same species. It ensures the continuity of life, maintains population balance, and allows genetic information to pass from one generation to the next.
Reproduction in biology is a core topic studied at school and college levels because it connects many biological concepts such as cell division, genetics, evolution, and development. Understanding reproduction helps students explain how organisms grow in number, how variation arises, and how species survive changing environments.
This article provides a complete, student-friendly explanation of reproduction in biology, covering definitions, types, biological processes, importance, diagrams explained in words, real-life examples, misconceptions, exam-oriented notes, practice questions, and FAQs.
Definition of Reproduction
What is Reproduction in Biology?
Reproduction in biology is the biological process by which living organisms produce new individuals similar to themselves. These new individuals are called offspring.
According to biological science, reproduction:
- Produces offspring
- Transfers genetic material
- Ensures survival of species
- Maintains life continuity
Reproduction is not essential for the survival of an individual organism, but it is essential for the survival of a species.
Why Reproduction Is a Fundamental Life Process
All living organisms share some common life processes such as nutrition, respiration, growth, excretion, and reproduction. Among these, reproduction is unique because:
- It ensures continuity of life
- It introduces genetic variation
- It supports evolution
- It maintains population stability
Without reproduction, a species would eventually become extinct after the death of its existing members.
Types of Reproduction in Biology
Based on the number of parents involved and the method of reproduction, reproduction in biology is classified into two main types:
1. Asexual Reproduction
2. Sexual Reproduction
Asexual Reproduction
Definition
Asexual reproduction is a type of reproduction in which only one parent is involved, and no fusion of gametes occurs. The offspring produced are genetically identical to the parent.
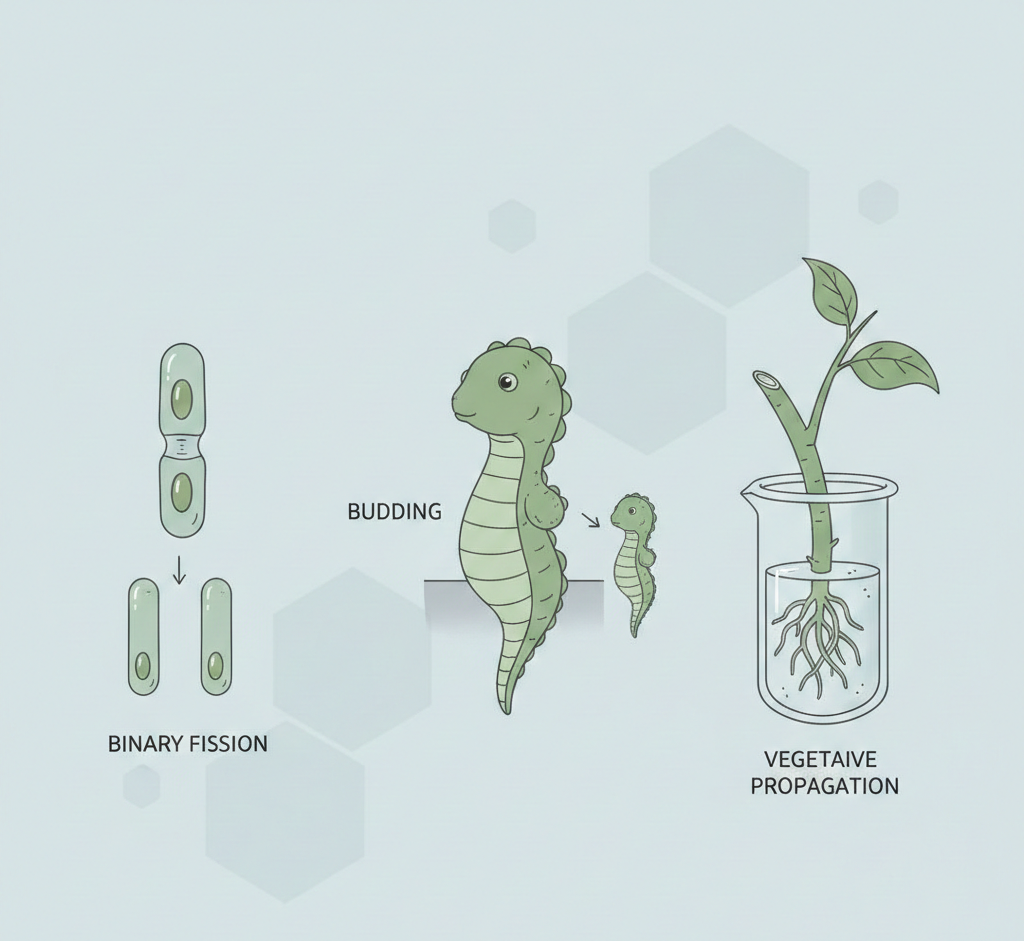
Key Characteristics of Asexual Reproduction
- Involves a single parent
- No formation of gametes
- No fertilization
- Offspring are genetically identical (clones)
- Rapid process
- Common in unicellular organisms
Types of Asexual Reproduction
1. Binary Fission
Binary fission is the simplest form of reproduction in biology seen in unicellular organisms like bacteria and Amoeba.
Steps involved:
- DNA replication
- Division of nucleus
- Division of cytoplasm
- Formation of two identical daughter cells
Example: Amoeba, bacteria
2. Multiple Fission
In multiple fission, the nucleus divides repeatedly to form many nuclei, followed by division of cytoplasm.
Example: Plasmodium
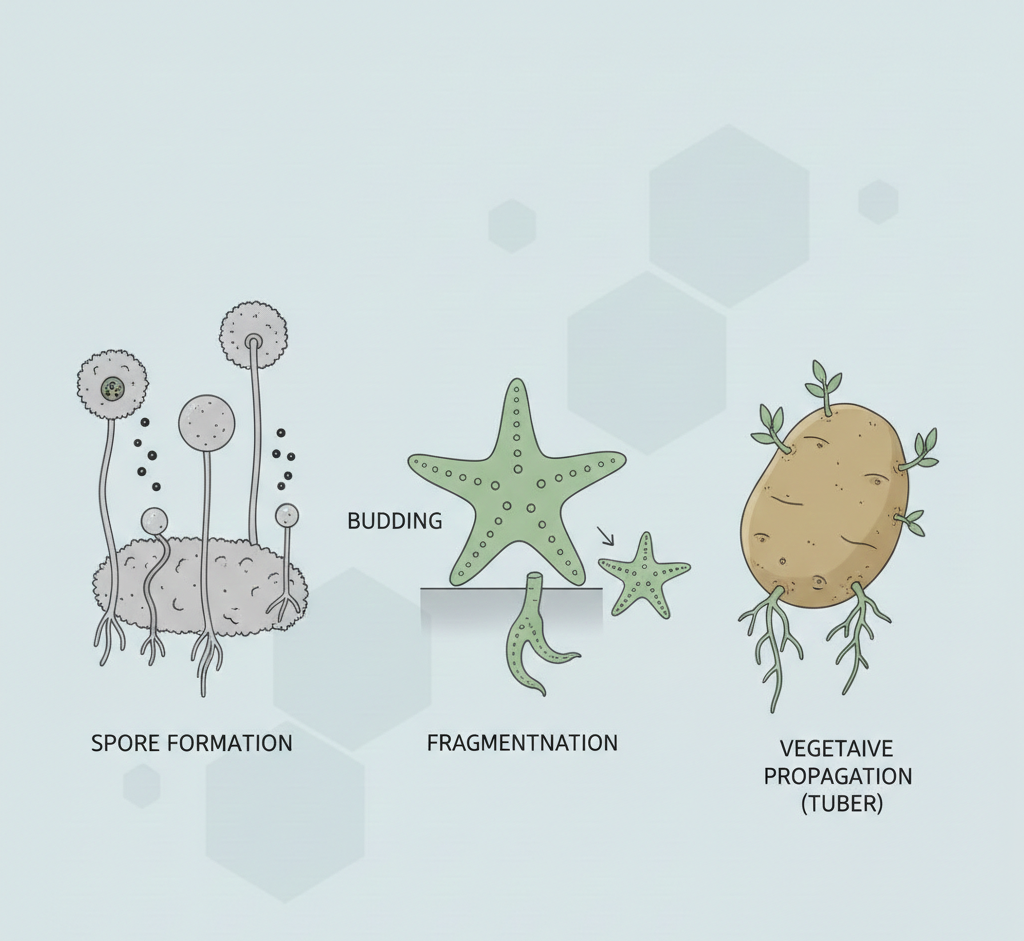
3. Budding
In budding, a small outgrowth called a bud develops on the parent body.
Steps:
- Bud formation
- Growth of bud
- Detachment from parent
Example: Yeast, Hydra
4. Fragmentation
The parent body breaks into fragments, and each fragment develops into a new organism.
Example: Spirogyra
5. Spore Formation
Spores are thick-walled reproductive structures that can survive harsh conditions.
Example: Rhizopus (bread mold)
Advantages of Asexual Reproduction
- Fast reproduction
- No need for a mate
- Large number of offspring
- Useful in stable environments
Disadvantages of Asexual Reproduction
- No genetic variation
- Poor adaptability to environmental changes
- Limited evolution
Sexual Reproduction
Definition
Sexual reproduction is a type of reproduction in biology that involves two parents and the fusion of male and female gametes to form a zygote.
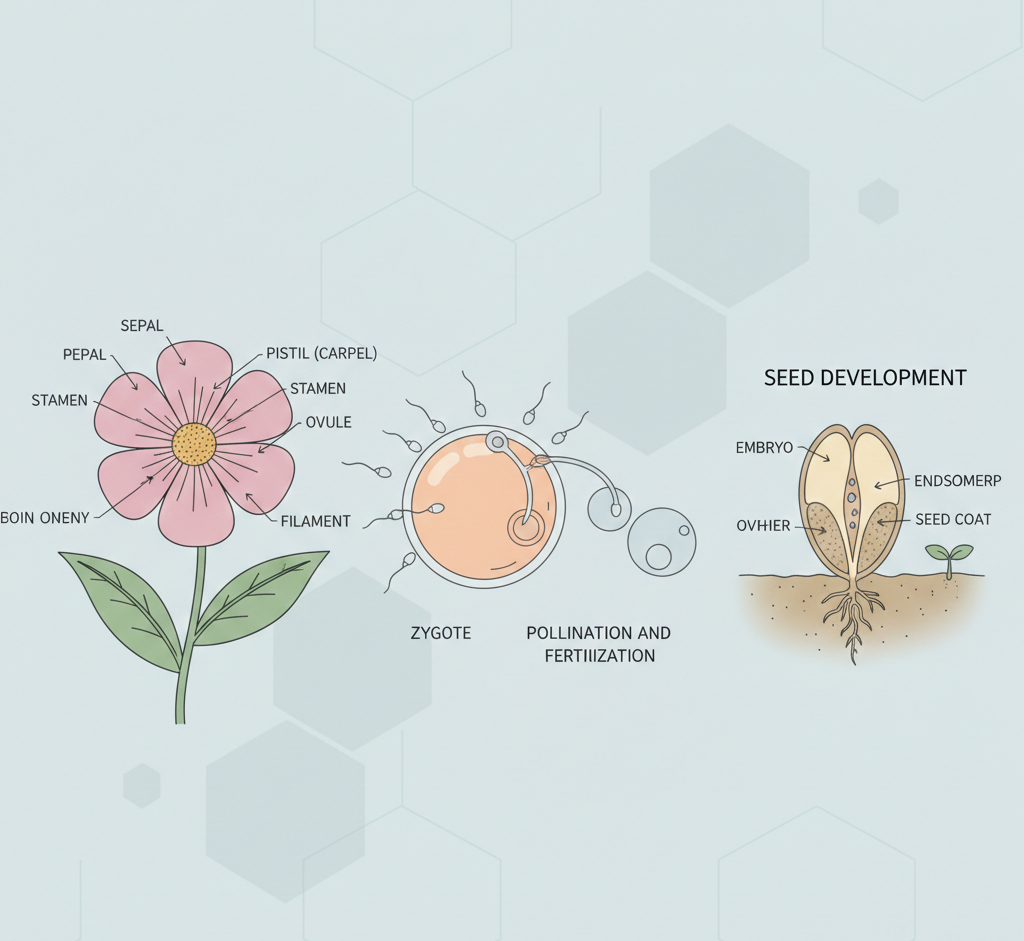
Key Features of Sexual Reproduction
- Involves two parents
- Formation of gametes
- Fertilization occurs
- Genetic variation present
- Slower process
Gametes and Their Role
Gametes are specialized reproductive cells:
- Male gamete: Sperm
- Female gamete: Ovum (egg)
Gametes are haploid (contain half the number of chromosomes).
Fertilization
What is Fertilization?
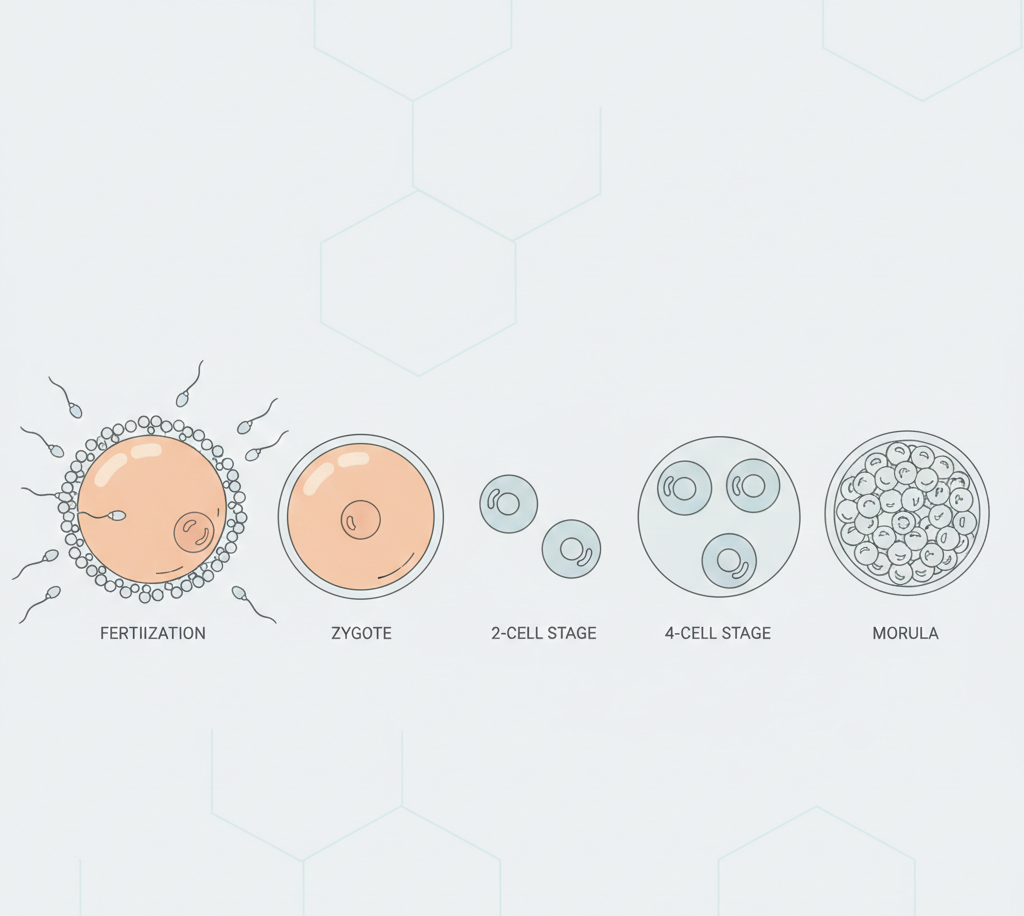
Fertilization is the fusion of male and female gametes resulting in the formation of a zygote.
Types of Fertilization
1. External Fertilization
- Occurs outside the body
- Requires water
- Produces many gametes
Example: Frogs, fish
2. Internal Fertilization
- Occurs inside the female body
- Fewer gametes
- Higher survival rate
Example: Humans, birds, mammals
Human Reproduction (Brief Overview)
Male Reproductive System
- Testes: Produce sperm
- Vas deferens: Transport sperm
- Penis: Transfers sperm
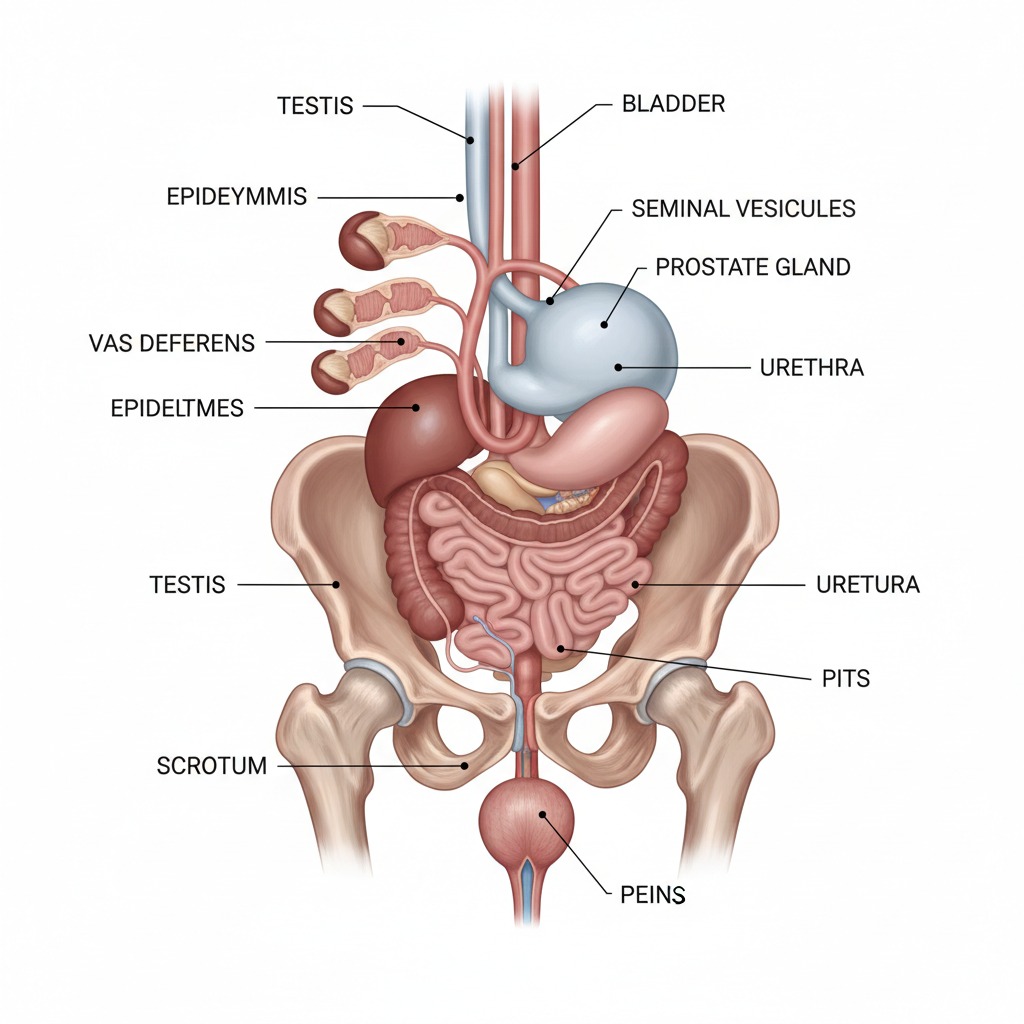
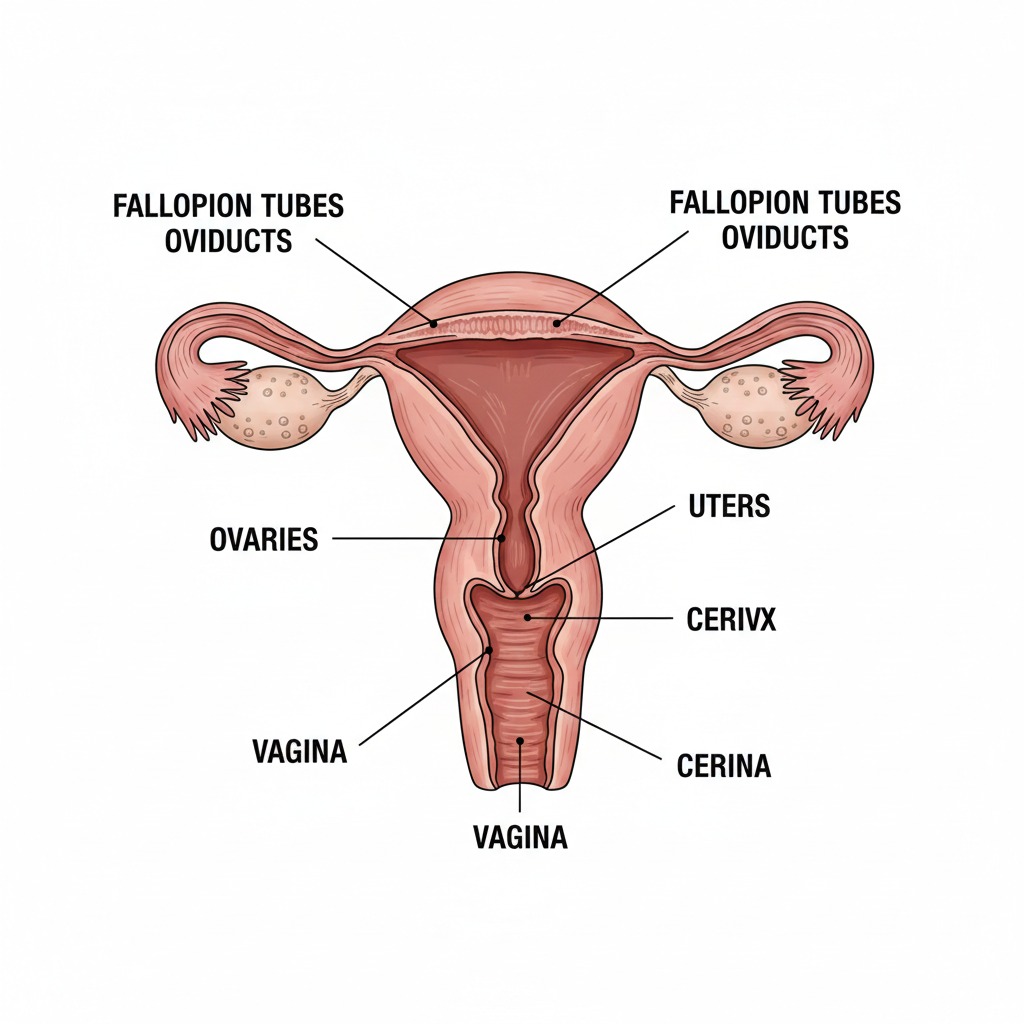
Female Reproductive System
- Ovaries: Produce eggs
- Fallopian tubes: Site of fertilization
- Uterus: Development of embryo
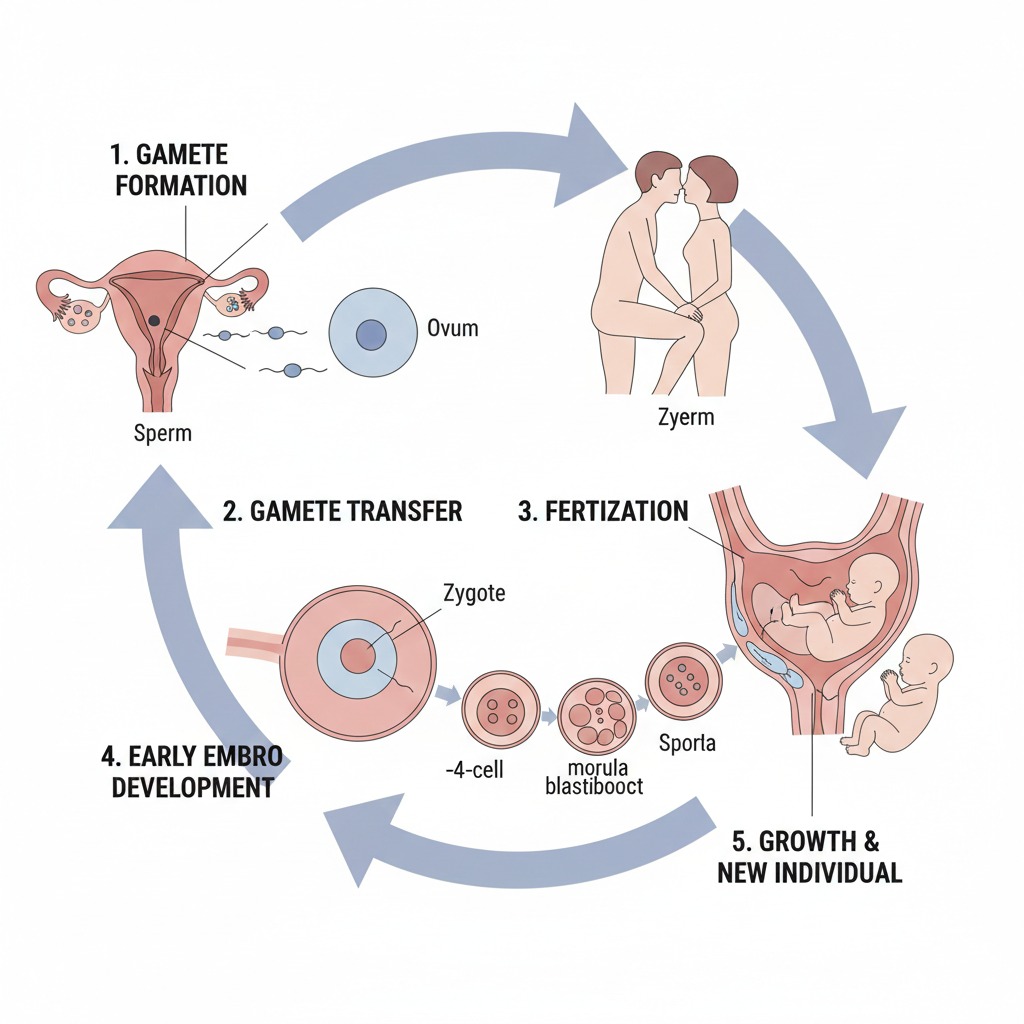
Steps in Sexual Reproduction
- Gamete formation (meiosis)
- Transfer of gametes
- Fertilization
- Zygote formation
- Embryo development
- Birth or hatching
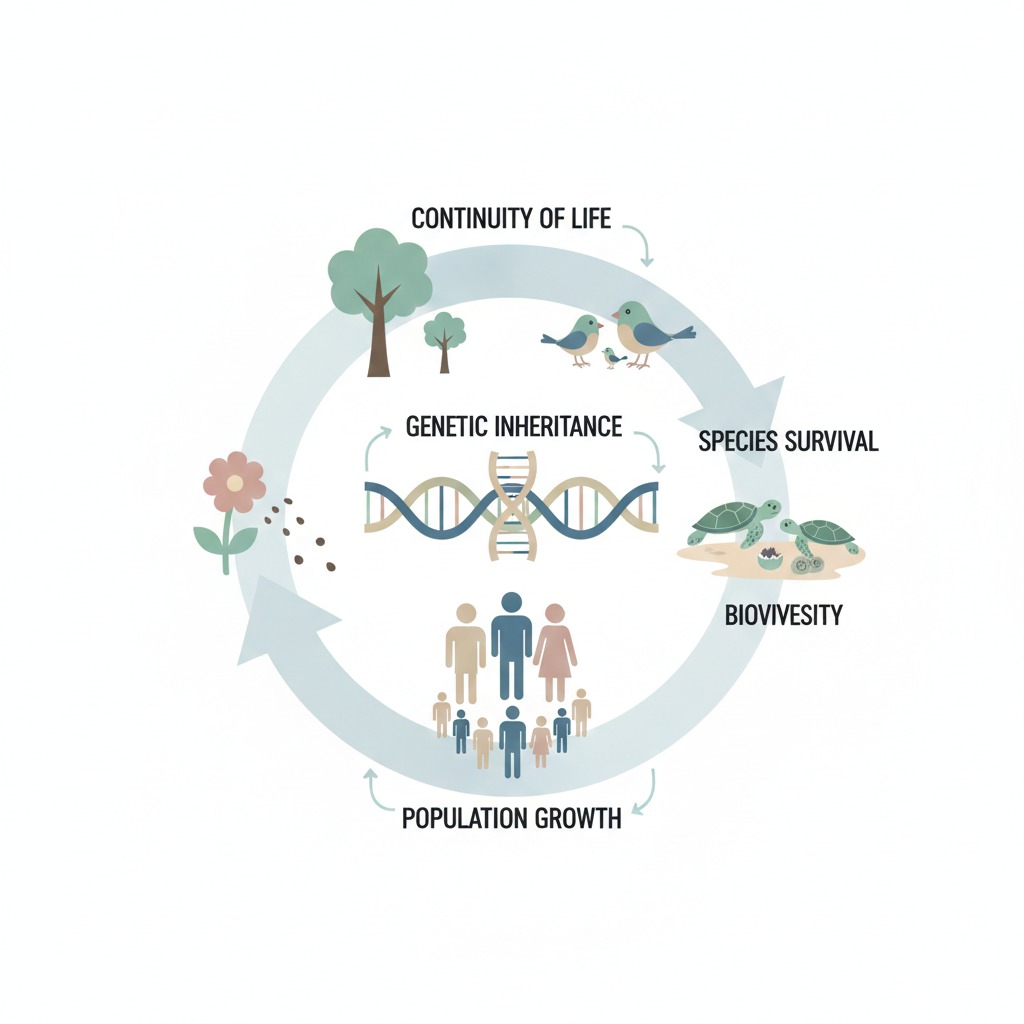
Importance of Reproduction in Biology
Reproduction in biology is important because it:
- Ensures species survival
- Maintains population balance
- Produces genetic variation
- Supports natural selection
- Drives evolution
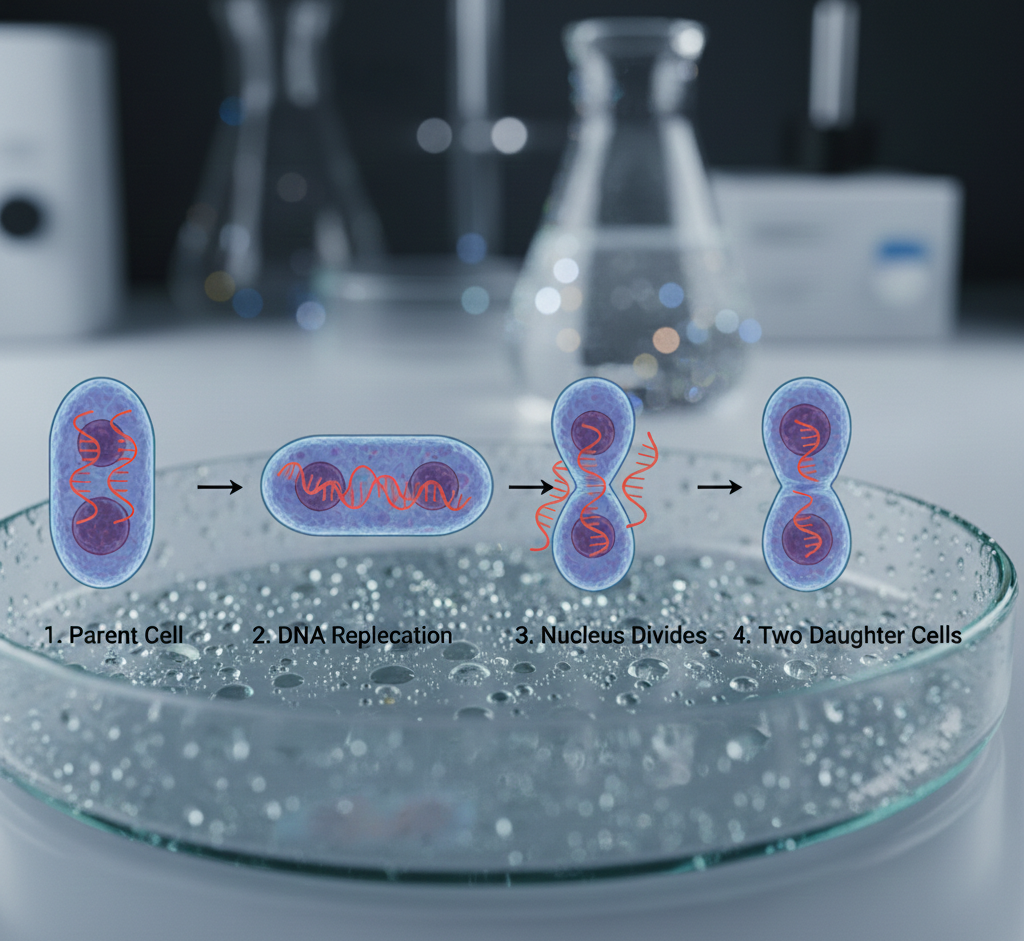
Diagrams Explained in Words
Binary Fission Diagram Explanation
- Parent cell in center
- Nucleus divides into two
- Cytoplasm splits
- Two identical daughter cells form
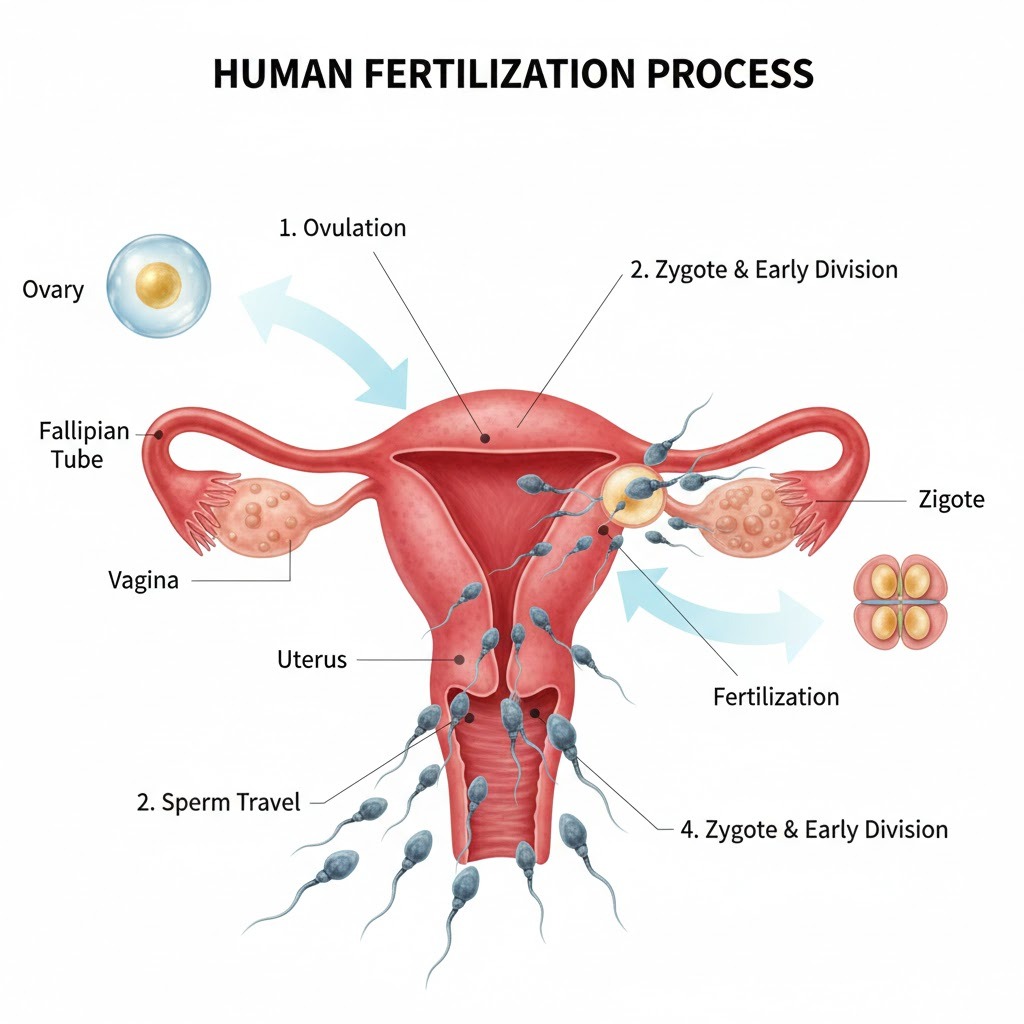
Human Fertilization Diagram Explanation
- Sperm travels through reproductive tract
- Fuses with egg in fallopian tube
- Zygote forms
- Zygote moves to uterus
Real-Life Examples of Reproduction
- Bacteria multiplying in food
- Plants reproducing by seeds
- Frogs laying eggs in ponds
- Humans giving birth to children
Common Mistakes and Misconceptions
- Reproduction is essential for individual survival (Incorrect)
- Asexual reproduction produces variation (Incorrect)
- All organisms reproduce sexually (Incorrect)
- Fertilization and reproduction are the same (Incorrect)
Exam-Oriented Notes
- Reproduction is a life process
- Two main types: Asexual and Sexual
- Asexual reproduction produces clones
- Sexual reproduction produces variation
- Fertilization forms a zygote
Practice Questions
Very Short Answer
- Define reproduction.
Answer: Reproduction is the process of producing new individuals of the same species. - Name one asexual method.
Answer: Binary fission
Short Answer
- Differentiate between asexual and sexual reproduction.
Answer: Asexual involves one parent and no variation; sexual involves two parents and variation.
Long Answer
- Explain sexual reproduction with steps.
Answer: Involves gamete formation, fertilization, zygote formation, and development.
Summary for Revision
Reproduction in biology is the process by which organisms produce offspring. It is essential for the survival of species. Reproduction is of two types: asexual and sexual. Asexual reproduction is fast and produces identical offspring, while sexual reproduction produces variation and supports evolution. Understanding reproduction helps explain continuity of life.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is reproduction in biology?
Reproduction is the process by which organisms produce new individuals.
2. Why is reproduction important?
It ensures survival and continuity of species.
3. What are the types of reproduction?
Asexual and sexual reproduction.
4. Which reproduction produces variation?
Sexual reproduction.
5. What is fertilization?
Fusion of male and female gametes.
6. Is reproduction necessary for individuals?
No, but it is necessary for species.
7. What is a zygote?
A zygote is the cell formed after fertilization.
Source